
Understanding your menstrual cycle
The menstrual cycle is much more than just your monthly period – it is a natural process that occurs in women and people assigned female at birth (AFAB) and typically begins when you start adolescence (around the age of 12). Every month, your reproductive system goes through a series of changes which are driven by your hormones - FSH, LH, oestrogen and progesterone - as your body prepares for pregnancy. You’ll learn more about what these hormones are below.
The four stages of the menstrual cycle
During your menstrual cycle, your body goes through four stages as it prepares itself for possible pregnancy. The average length of a menstrual cycle is 28 days but some variation is completely normal and menstrual cycles typically range from 21 to 35 days in length.
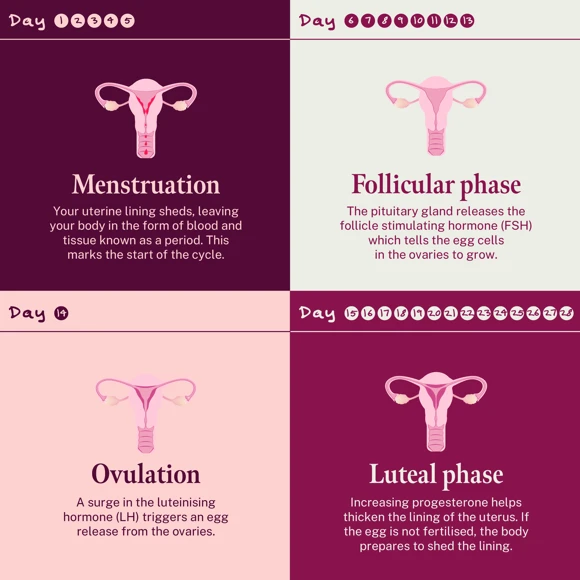
Menstruation
Commonly referred to as a period, menstruation marks the beginning of your menstrual cycle. When the egg hasn’t been fertilised by sperm, your uterine lining sheds, leaving your body in the form of blood and tissue known as a period .
If you’re tracking your period , you count the first day of vaginal bleeding as day one. Your period will typically last around two to seven days and during this time, you may lose around 30 to 40ml of blood.
However, up to 30% of people who menstruate experience heavy periods, known as menorrhagia and can lose 80ml or more. If you suffer with heavy periods and you’re looking for some relief, you may be able to try Evana® Heavy Period Relief, a non-hormonal treatment for heavy bleeding containing the active ingredient tranexamic acid that can reduce menstrual bleeding by up to 60%.
While in the menstruation phase, you might experience some discomfort. Common symptoms can include:
- Abdominal cramps
- Headaches
- Back pain
- Changes in mood
- Bloating
- Fatigue
- Weakened immune system
Period pain, also known as dysmenorrhoea, affects up to 91% of young women. Taking the form of a cramping pain in your tummy that can spread to your thighs and back, dysmenorrhoea can impact on your everyday life. To help manage period pain, you may be able to try medication such as Ultravana® Period Pain Relief, an anti-inflammatory drug containing the active ingredient naproxen, which can offer up to 12 hours relief from period pain .
Follicular phase
The follicular phase starts on the first day of the period and lasts until ovulation, which usually occurs around day 14, in the middle of the menstrual cycle. During this time, the pituitary gland releases the follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) which tells the egg cells in the ovaries to grow. As the eggs mature, inside sacs known as t follicles, The hormone, oestrogen is released.
Symptoms of the follicular phase can include:
- More potential for muscle adaptation
- Increased ability to recover from exercise and training
- Increased energy levels
- Tendency for sexual interest
- A shift towards positive mood in the later follicular phase.
Ovulation
The next phase in the menstrual cycle is ovulation which happens after a surge in the luteinising hormone (LH) when the egg is released from the ovaries . The egg will then live for between 12 and 24 hours after ovulation has occurred. During this time, a sperm can meet and fertilise an egg, resulting in pregnancy.
Luteal phase
After ovulation is the start of your luteal phase, which lasts until your next period. Typically, this is around 14 days. Once the egg has left the ovary, it travels along the fallopian tube that connects the ovary to the uterus. If it is not fertilised, the egg will die as the body prepares itself for the next menstrual cycle.
The empty follicle that housed the egg will then turn into a temporary gland known as the corpus luteum. This produces progesterone and will continue to do so if the egg is fertilised until eight weeks into the pregnancy. If it isn’t, the corpus luteum will stop producing these hormones.
During the luteal or premenstrual phase, some women can experience premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD). Around 30% of women suffer moderate to severe PMS and 5 to 8% suffer from PMDD.
Symptoms of PMS can include:
- Mood swings
- Feelings of anxiety and irritation
- Fatigue
- Bloating
- Breast tenderness
- Headaches
- Greasy hair
- Spotty skin
- Appetite changes.
PMDD symptoms are similar to those of PMS but are generally more intense and have a larger impact on your day to day life. These symptoms can include:
- Joint and muscle pain
- Cramps
- Binge eating
- Difficulty sleeping
- Depression
- Suicidal thoughts (in severe cases).
Browse our website to learn more about the menstrual cycle and products you can use to provide relief from disruptive periods.
Menstrual health products
Do you suffer with disruptive periods?
Our menstrual health products are designed to provide effective relief from heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) and period pain, helping you to get on with your life.
Evana Heavy Period Relief Tablets and Ultravana Period Pain Relief Tablets are easily accessible both online and from a range of pharmacies without the need for a prescription.
Explore our website to find out more about our period medicines.
-

Find relief from heavy periods
Buy Evana -

Find relief from painful periods
Buy Ultravana
Sign up to our mailing list for exclusive content and updates
